But what does it really mean?
And more importantly, how can it help you or your business get more done with less hassle?
AI agents are no longer just experimental tools. They’re being used across industries—from automating support emails to analyzing trends in financial data.
The trick isn’t just in using them but in integrating them properly into the day-to-day workflow so they become genuinely helpful instead of just a shiny new gadget.
According to the S&S Insider the AI agents market was valued at $3.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $103.6 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 44.9% from 2024 to 2032
In this article, I’ll break down everything you need to know about integrating AI agents into your business or personal processes.
Whether you’re managing a team, building products, running operations, or just looking for ways to get more done without burning out, this guide will walk you through how to make AI agents work for you—not the other way around.
What Is an AI Agent, Really?
Let’s start with the basics.
An AI agent is a program that performs tasks for you or on your behalf using artificial intelligence. Unlike traditional automation tools that follow set rules, AI agents can understand context, learn from data, and make decisions—or at least suggestions—based on what they “see.”
Some examples you might recognize:
- Siri or Google Assistant that responds to your voice commands
- Chatbots on websites that help answer customer queries
- GitHub Copilot which helps developers write code
- AI assistants automatically identify an available slot for a meeting.
These tools are built using different types of AI, like natural language processing (to understand language) or machine learning (to improve over time). And when you integrate them into workflows, they can do a lot more than just one-off tasks.
You can think of them like digital assistants that live inside your systems. They can connect the dots between tools, handle repetitive stuff, and make your overall workflow feel smoother.
Why Integrate AI Agents at All?
Alright, but why bother?
In my experience, teams spend a lot of time doing things that don’t really need a human touch:
- Copying and pasting data between tools
- Checking emails or dashboards constantly
- Sorting messages or support tickets
- Updating spreadsheets manually
AI agents take over these kinds of tasks. But integration is where the real value lies. When they’re connected to your existing tools—email, CRM, task managers, analytics platforms—they can:
- Automatically move information from one platform to another.
- React in real-time to certain triggers (like an email arriving or a lead filling out a form)
- Act based on rules or past behavior (like scheduling meetings based on preferences)
This kind of behind-the-scenes automation can:
- Save hours every week
- Cut down on human errors
- Let your team focus on actual problem-solving instead of busywork
Types of AI Agents You Can Use
Not all AI agents are created equal. Depending on what you’re trying to accomplish, different types of agents serve different purposes. Let’s break it down with a bit more detail:
1. Reactive Agents
These are the most basic kind. These kinds of AI agents don’t learn from past experience or remember past interactions. They just react to a specific input in a fixed way.
Think of it like this: You click a button, and they perform a pre-programmed action. That’s it. For example, a chatbot that only gives set responses when you type specific keywords.
You’ll find reactive agents used in simple automated replies, rules-based bots, or even IoT devices that turn on/off based on input without adapting to patterns.
They’re fast, efficient, and often reliable—but not flexible. If you need dynamic decision-making or learning over time, you’ll want something more advanced.
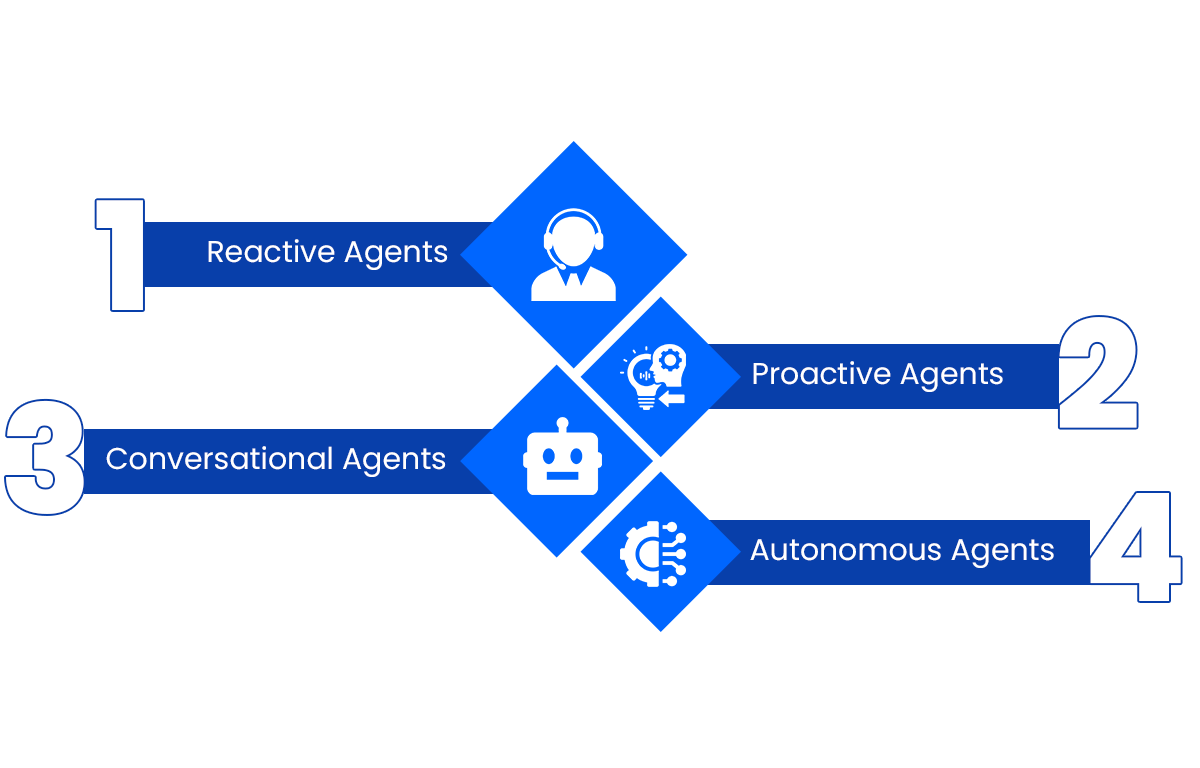
2. Proactive Agents
These agents don’t just wait around for you to give them something to do. They take initiative.
For instance, a sales agent that keeps an eye on your CRM and notifies you the moment a lead becomes active again— or if they visit your pricing page several times in a short span.
They’re useful when you want the system to alert you about things you might miss. Think of it as the difference between a reminder app and an actual assistant who says, “Hey, based on this pattern, you might want to follow up.”
They often combine rule-based behavior with a bit of pattern recognition. The goal is to surface insights or take action before you even ask.
3. Conversational Agents
This is probably the most familiar type. These agents can talk to you in plain language. They're trained in natural language processing (NLP), so they can handle multi-step conversations and respond in a way that feels human—at least most of the time.
They’re behind tools like:
- Website chatbots that help answer common customer questions
- Virtual assistants like Alexa or Google Assistant
- In-app support agents in platforms like Intercom or Drift
Good conversational agents don’t just spit out canned answers. They try to understand context, follow up with clarifying questions, and guide you through a task or solution. At the same time, conversational ai can help manage complex interactions by deciding when to transfer the conversation to a human.
Some of them can also pass off the conversation to a human when things get too complex— so your users don’t get stuck.
4. Autonomous Agents
Now we’re talking next-level stuff. Autonomous agents can operate independently on their own, without any assistance from humans.
You’ll find them in advanced use cases like:
- Self-driving cars that navigate roads and react to traffic conditions
- Automated trading bots that buy or sell based on market signals
- Warehouse robots that sort, pick, and move products with little to no oversight
They often use reinforcement learning or multi-agent systems to adapt over time. These are the agents that act more like independent workers rather than assistants.
They’re powerful but also riskier if not managed properly. So most businesses start with simpler types first before deploying autonomous agents in critical tasks.
Curious about what AI agents can actually do?
Check out our blog on 10 real-world applications of AI agents that are transforming industries—from customer support to marketing.
Explore Use CasesThe Building Blocks of AI Agent Integration
Before we get into how to build these workflows, let’s break down what brings agents and your digital life together:
1. APIs (Application Programming Interfaces)
APIs are like translators. They let different programs “talk” with each other. AI agents use APIs to connect to email clients, calendars, databases, or even your smart fridge.
Simple example: Your AI assistant checks your Google Calendar using Google’s API and reminds you of meetings.
2. Data Connectors
Agents need access to the right data. Connectors provide the bridge—pulling data from spreadsheets, cloud storage, or messaging apps.
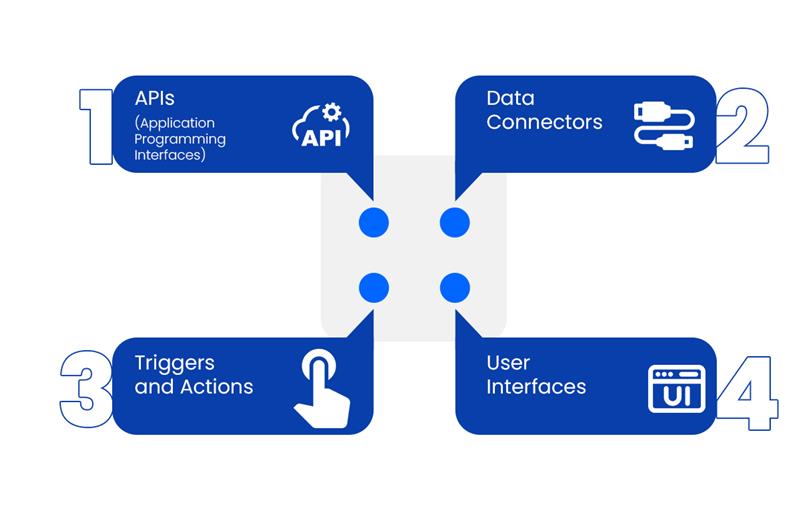
3. Triggers and Actions
Think of a trigger as the green light. When something happens (a new email arrives, a file is updated), it “triggers” the agent to do its job—like classify the email or copy the file.
4. User Interfaces
Sometimes you’ll interact with agents via chat windows, voice commands, or dashboards. These interfaces make it easy for you to see what’s happening or tell the agent what you want.
Key Benefits for Businesses and Individuals
It’s not just about being “high tech.” Real benefits include:
- Time Savings: Let AI handle the grunt work, so you spend more time on things that require human ingenuity.
- Fewer Errors: Machines don’t get tired. If you set them up right, repetitive mistakes go away.
- Better Consistency: Agents don’t forget, get distracted, or go on vacation.
- Around-the-Clock Service: Good news for support teams—AI doesn’t sleep.
Steps to Integrate AI Agents Into Your Workflow
Let’s get into each step of getting AI agents up and running at work, breaking it down so it’s practical and clear.
1. Spot the Repetitive Tasks
Start by looking closely at your daily work. Find things you or your team do over and over. This could be entering information, sorting emails, tracking orders, updating documents, or following up with clients. Adding processes like email verification ensures that communications reach the right people, reducing wasted effort and keeping workflows more efficient.
- Keep an eye out for patterns that slow things down.
- Jot down anything that makes you think, “There must be a better way.”
- Ask your team where their time gets eaten up, especially by simple yet essential tasks.
All you need is a pen and paper or whatever note-taking method works for you. Put together a list of tasks that are routine and don’t need a lot of decision-making.
2. Pick the Right Agent (or Build Your Own)
There are plenty of agents already designed for common processes such as scheduling, sending reminders, or managing customer interactions. Sometimes, you may need something more specialized and want to train or build a custom one.
- Pre-designed agents often come with many tools used in everyday office software.
- If your needs are different, look for options where you can customize an agent or get help from IT or a developer.
- Focus on agents that work easily with what you already use and directly address a real need.
- If you’re working in an organization, check what tools and systems are already approved or supported.
3. Connect the Dots (APIs and Data)
This part is about letting the agent interact with your essential tools—like calendars or databases. Sometimes you can just sign in and connect your work apps in a few clicks. Other times, a bit of tech support helps.
- Make sure you only share data that’s necessary for the task.
- If your info is scattered or messy, a little tidy-up now saves headaches later.
- Start with one connection or workflow, then expand as you see progress.
4. Set Up Triggers and Rules
Triggers are what signal the agent to start working. Think: “If this happens, then do that.” Set rules for when the agent should jump in, like a new message or a task added to a list.
- Take time to define clear boundaries so the agent doesn’t respond to the wrong things.
- Test it with safe information first to catch any surprises before it goes live in your real workflow.
- Get feedback from others to make sure your triggers make sense.
5. Monitor and Adjust
Agents need a little babysitting, especially at first.
- Watch how things run for at least a week.
- Is it catching the right things? Missing stuff? Annoying your team or customers?
- Adjust your settings or rules as you notice issues—most platforms let you make quick changes.
- If the agent interacts with anyone outside your team, check that its responses are friendly and easy to understand.
6. Keep Data Safe
Because agents can access a lot of information, protection matters.
- Only give the agent access to what it really needs, not more.
- Use strong security practices for any accounts or credentials you share.
- Review who can see what and update permissions when things change or team members leave.
- Treat any unique codes, keys, or logins as private as you would your home password.
- If you manage sensitive info, consider getting guidance from someone in charge of security or compliance.
7. Train Your Team
Success depends on people understanding and cooperating with these new helpers. To support training, AI charts for PowerPoint can visually demonstrate processes, workflows, or AI agent functions, making it easier for the team to grasp complex concepts.
- Show the team what the agent does and how they can work alongside it.
- Invite feedback, especially early on. Your coworkers often notice things you might not.
- Make simple guides or quick notes as a reference, especially if the process changes.
Mistakes to Avoid When Getting Started
1. Automating Too Much Too Soon
When you’re excited about AI, it’s tempting to try and automate every part of your workflow all at once. But this approach often backfires.
Why it’s a mistake: Taking on too many workflows before you’ve tested and refined them can lead to confusion, errors, and frustration. If something goes wrong, it’s harder to find the problem because everything is mixed together.
Better approach: Start with just one or two simple, repetitive tasks that clearly need saving time. Get those workflows running smoothly and make sure they do exactly what you want. Once you’re confident those work well, then add more.
Benefit: This step-by-step build helps you learn as you go and avoids overwhelming yourself or your team.
2. Skipping Human Approval
Some people assume that once AI agents are set up, they can be left completely alone. This is especially risky for tasks involving communication, money, or sensitive decisions.
Why it’s a mistake: AI agents aren’t perfect. They can misunderstand context or make mistakes, especially early on. If you let an AI send emails directly to clients or approve payments without review, errors might slip through.
Better approach: Keep a human “in the loop” for important steps—like reviewing outgoing messages, financial approvals, or any actions that directly impact customers or finances.
Benefit: This safety net prevents avoidable mistakes and builds confidence in the system while it learns.
3. Ignoring Security
AI agents often need access to important data—emails, calendars, files—that could be sensitive. Overlooking security risks can lead to data breaches or privacy violations.
Why it’s a mistake: If you use platforms without strong security measures or fail to limit what agents can access, you might expose personal or company information to unauthorized users.
Better approach: Choose reputable AI and automation platforms that encrypt data and allow tight control over permissions. Regularly review what the agents can see and do.
Benefit: Protecting your data keeps your business safe, meets compliance requirements, and maintains trust with colleagues and customers.
4. Not Training Your Team
Sometimes, bosses or managers install AI agents and expect the team to figure out how to use them. This causes confusion, resistance, or misuse.
Why it’s a mistake: If people don’t understand what the AI does or how to interact with it, they might ignore it, make incorrect assumptions, or use it the wrong way.
Better approach: Take time to explain the AI’s role, show how to work alongside it, and encourage questions. Provide updates as the system evolves.
Benefit: Well-informed teams are more likely to embrace AI as a helpful tool, reducing mistakes and improving overall workflow.
What’s Coming Next for AI Agents?
We’re seeing a shift from “one big AI assistant” to smaller, specialized agents that can collaborate.
Instead of one tool doing everything, you’ll have:
- A research agent that gathers info
- A calendar agent that manages your meetings
- A customer success agent that monitors user feedback
These agents will start talking to each other. For example, your research agent might hand off a summary to your writing agent, which then drafts a blog post.
That’s where things start to feel less robotic and more like you have a real team helping you out.
Want to automate repetitive tasks and build smarter workflows with AI agents?
Our AI experts at Zenesys can help you design and deploy custom AI agents that boost productivity and reduce manual work.
Build Your AI AgentCommon Questions People Ask
Do I need to code to integrate AI agents?
Not necessarily. Many platforms offer no-code or low-code solutions. That said, for custom workflows, some coding might help.
What tools can I connect AI agents to?
If the tool has an API or is supported by integration platforms like Zapier, Make.com, or Pipedream, you’re good to go. Gmail, Slack, Notion, HubSpot, Salesforce—you name it.
Is AI safe to use for sensitive tasks?
Yes, but you need to take precautions. Use platforms with strong security policies, encrypt your data, and add manual approvals where needed.
Will AI replace my job?
Generally, AI agents handle repetitive, low-value tasks. Most people find their jobs change—not disappear. You get more time for creative or people-focused work.
How Zenesys Can Help You Build Smarter Workflows with AI Agents
Let's talk about what Zenesys actually does for you—not in theory, but in practice.
Finding the Right Problems to Solve
You probably have a hundred things you could automate. But where do you start? Zenesys sits down with you to identify which tasks are actually draining your time and budget.
They look at your daily operations—data entry, email sorting, ticket management, report generation—and pinpoint where AI agents can make the biggest impact right away. No guessing. No wasted effort on things that don't move the needle.
Building AI That Fits Your Business
Generic chatbots only go so far. What happens when your business has specific processes, industry requirements, or unique customer needs? Zenesys creates custom AI agents that understand your exact workflows.
Whether you need agents to handle appointment scheduling, process invoices, qualify leads, or monitor inventory levels, they design solutions around what you actually do—not what some template assumes. Your business gets an AI assistant that knows your systems, your data, and your goals.
Making Your Tools Work Together
Here's a common headache: your team uses five different platforms, and information lives in separate silos. Zenesys connects your AI agents directly to your CRM, accounting software, project management tools, and communication platforms.
This means data flows automatically between systems. When a customer fills out a form, the agent can update your CRM, notify your sales team, and schedule a follow-up—all without anyone lifting a finger. No more copying information from one place to another.
Letting Your Team Focus on What Matters
Think about how much time goes into repetitive work. Reading every support email. Updating spreadsheets. Checking dashboards. Sorting through notifications. Zenesys helps you hand off these routine tasks to AI agents so your team can spend time on strategy, creativity, and solving complex problems.
The goal isn't just efficiency. It's giving people back their time for work that actually requires human judgment and expertise.
Starting Simple, Growing Steadily
You don't need to transform your entire operation overnight. Zenesys helps you begin with one or two straightforward workflows—maybe automating customer inquiries or organizing incoming data.
Once those are running smoothly and your team feels comfortable, you expand. Add more agents. Connect more tools. Take on bigger processes. This gradual approach reduces risk and lets you see real results before committing to larger changes.
Keeping Everything Secure
When AI agents access your business data, security can't be an afterthought. Zenesys builds solutions that follow proper security protocols, encrypt sensitive information, and limit what agents can access.
They also help ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR if you're handling customer data. Your information stays protected, and you maintain control over who sees what.
Providing Support When You Need It
AI agents require ongoing attention. Performance monitoring. Adjustments based on feedback. Updates when business processes change. Zenesys offers round-the-clock support so you're not left figuring things out alone.
When something needs tweaking or you want to add new capabilities, there's a team ready to help. Your AI agents evolve as your business grows.
Training Your Team to Work Alongside AI
Technology only works when people know how to use it. Zenesys provides training so your team understands what the AI agents do, how to collaborate with them, and when to step in.
This prevents confusion, builds confidence, and ensures everyone benefits from the new system instead of fighting against it.
Delivering Measurable Results
At the end of the day, AI agents should save you time and money. Zenesys focuses on creating agents that produce tangible outcomes—fewer hours spent on manual work, faster response times, reduced errors, and better customer experiences.
You get tools that work in the background, handling the repetitive stuff, so your business runs smoother and your team stays focused on growth.
The Real Difference
Zenesys doesn't just sell you software and walk away. They partner with you through the entire journey—from identifying opportunities to building custom agents, connecting systems, training staff, and providing ongoing support.
You get AI agents designed specifically for your challenges, integrated with your existing tools, and backed by a team that understands both the technology and your business needs.
Wrapping It Up
Once you see the results, it’ll be easier to expand into other areas. The best part? These agents don’t need sleep, don’t complain, and only get better the more you use them.
If you’ve been wondering whether it’s worth setting up AI integrations—my honest answer? Try one small thing. You might be surprised how helpful it is.


.webp?lang=en-US&ext=.webp)

.webp?lang=en-US&ext=.webp)

