Building a healthcare app that rivals TATA 1MG feels like a distant dream for most entrepreneurs. Yet, the numbers tell a different story.
According to Statista, healthcare applications constitute over 18% of the app market and global investment in the category exceeds $42 billion.
Data from 2025 estimates the global mHealth apps market size at $43.28 billion, with the broader digital health market projected at $163.06 billion, and over 1.4 billion users expected.
The real question isn't whether you can build an app like TATA 1MG—it's how much you should budget and where your money actually goes.
TATA 1MG stands as India's largest online pharmacy and healthcare platform. It connects millions of users with medicines, diagnostic services, and healthcare consultations. What makes this app valuable isn't just the idea.
It's the infrastructure, technology stack, regulatory compliance, and team expertise behind it. If you're thinking about entering the healthcare app development space or building something similar, you need to understand the true costs involved.
This article breaks down everything you need to know about building an app like TATA 1MG in 2025. We'll explore the real expenses.
We'll uncover hidden costs you might miss. And we'll show you where your investment actually goes. Whether you're a startup founder, an investor, or a healthcare entrepreneur, this guide will give you clarity on what it takes to build a world-class healthcare application.
Key Takeaways
- Total development cost ranges from $500,000 to $3,000,000+ depending on complexity, team location, and feature set.
- Team size matters more than timeline: A skilled team of 8-12 developers takes 12-18 months, while larger teams finish faster but cost more.
- Backend infrastructure and compliance dominate the budget: Healthcare regulations and server costs eat up 25-35% of total expenses.
- MVP strategy saves money: Building a minimum viable product with core features costs $250,000-$500,000 and helps validate your idea before scaling.
- Choosing between in-house and outsourced teams changes everything: India-based outsourcing saves 40-60% compared to US or European teams.
Why Healthcare Apps Cost So Much?
The Complexity Factor
Healthcare apps aren't like social media platforms or food delivery apps. They deal with human lives. They store personal medical information. They require multiple regulatory approvals. This complexity drives up costs in ways other app categories don't experience.
Every feature needs to be bulletproof. A small bug in a music streaming app annoys users. A small bug in a healthcare app puts lives at risk. This is why healthcare app development services demand higher standards, more testing, and more rigorous quality assurance.
Data security becomes non-negotiable.
Regulatory requirements vary by country.
In India, apps must comply with HIPAA guidelines, GDPR (if users are in Europe), and India's Digital Personal Data Protection Act. Each regulation adds development time and cost. You can't cut corners on compliance because the penalties are severe.
The Team You Need
Building TATA 1MG requires more than just good developers. You need specialists. Let me break this down for you.
- 2-3 backend engineers (building the server-side logic)
- 2-3 frontend engineers (creating the user interface)
- 1-2 mobile developers (for iOS and Android apps)
- 1 DevOps engineer (managing infrastructure)
- 1 QA lead with 3-5 quality assurance specialists
- 1 project manager
- 1 healthcare compliance specialist
- 1 security engineer
That's roughly 13-15 people minimum. Each person has a different salary expectation. A senior healthcare backend engineer in India earns $40,000-$60,000 annually. In the US or Europe, they earn $120,000-$180,000 annually. The location of your team dramatically affects your budget.
Why can't you do this with fewer people? Healthcare apps require different skill sets than regular apps. Your backend engineer needs to understand HIPAA compliance. Your frontend developer needs to design intuitive health interfaces. Your QA specialist needs healthcare domain knowledge. Generalists won't cut it in this space.
Uncertain About Your Healthcare App Budget?
Stop guessing. With 14+ years of healthcare app development expertise, Zenesys Solutions Inc transforms vague ideas into precise cost estimates and detailed roadmaps. Connect with our team to learn exactly what your app will cost and what it takes to succeed.
Discuss Your Healthcare App IdeaBreaking Down the Real Costs in 2025
Development Costs
This is the biggest expense item. Let's be specific about what you're paying for.
Backend development involves building servers, databases, and APIs that power your app. For an app like TATA 1MG, you need robust infrastructure that handles millions of transactions daily. In India, backend development costs $80,000-$150,000. In the US, the same work costs $200,000-$400,000.
Frontend development is building the visual interface users see and interact with. This includes the website and admin dashboard. The cost range is similar to backend—$80,000-$150,000 in India, $200,000-$400,000 in the US.
Mobile app development deserves special attention because users expect flawless mobile experiences. Building separate iOS and Android apps (or using cross-platform solutions) costs $120,000-$250,000 in India and $300,000-$600,000 in the US.
Integration costs stack up quickly. You need to integrate payment gateways like Razorpay or Stripe. You need to connect to pharmaceutical databases. You need to link diagnostic centers. Each integration takes time and money—expect $30,000-$60,000 for all integrations.
Testing and QA is often underestimated. Healthcare apps require extensive testing. You're looking at $40,000-$100,000 just for quality assurance. This includes manual testing, automated testing, security testing, and load testing.
Total development cost in India ranges from $350,000 to $800,000. In the US or Europe, it ranges from $900,000 to $2,000,000. The difference comes down to labor costs and team experience levels.
Infrastructure and Hosting
Cloud hosting costs depend on user scale. If you're starting with 100,000 users, expect $2,000-$5,000 monthly. At 1 million users, you're paying $15,000-$40,000 monthly. TATA 1MG likely pays $100,000+ monthly for their infrastructure.
What are you paying for exactly? Server uptime, data storage, backup systems, CDN (content delivery networks), and security monitoring. Healthcare apps can't have downtime. Your infrastructure must be redundant and reliable. This reliability costs money.
Database costs add another layer. Encrypted databases that handle sensitive health information aren't cheap. You're looking at $1,000-$3,000 monthly for a properly secured healthcare database that scales with your user base.
First-year infrastructure costs total $50,000-$150,000, depending on expected user growth. This doesn't include development—it's just keeping the lights on.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal
Compliance documentation is tedious but necessary. You need privacy policies, terms of service, data protection frameworks, and healthcare-specific compliance documents. Hiring lawyers to create these costs $15,000-$40,000.
HIPAA compliance setup requires security audits, encryption implementation, and access control systems. If you're serving US users, this is mandatory. Budget $20,000-$50,000 for HIPAA implementation and certification.
Data Protection Act compliance (India's DPDP Act) requires similar safeguards. Budget $10,000-$25,000 for implementation.
Regular compliance audits happen annually. Each audit costs $5,000-$15,000. These audits verify you're following all healthcare regulations. They're not optional—they're essential.
Total first-year compliance costs: $50,000-$130,000.
Design and User Experience
UI/UX design is where your app becomes usable or unusable. Healthcare interfaces are challenging to design. Users range from tech-savvy young people to elderly patients. Your design must work for everyone.
A dedicated design team (1-2 designers plus a UX researcher) costs $50,000-$120,000 for the initial design phase. They create wireframes, prototypes, design systems, and user testing reports.
Why does design matter so much? People ignore beautiful apps if they're confusing. People abandon ugly apps even if they work perfectly. Healthcare apps especially need intuitive design because users might be stressed, ill, or in a hurry. Good design reduces support costs and improves adoption rates.
Third-Party Services and Integrations
- Payment gateway integration costs $5,000-$15,000. You need to accept multiple payment methods—credit cards, debit cards, digital wallets, net banking. Each method requires separate integration.
- Prescription verification systems connect to government pharmacy databases. This integration costs $10,000-$25,000 depending on the database complexity.
- Diagnostic center network requires building connections with hundreds of labs. Budget $15,000-$40,000 for this integration work.
- SMS and email services for notifications and order updates cost $5,000-$15,000 annually.
- Analytics and monitoring tools (like Firebase, Mixpanel) cost $2,000-$8,000 annually.
Total third-party service costs: $40,000-$100,000.
Marketing and Launch
App store optimization ensures your app appears in searches. This costs $5,000-$15,000 for initial setup.
Launch marketing campaign builds initial traction. Budget $30,000-$100,000 for launch ads, influencer partnerships, and PR.
First-year marketing costs total: $50,000-$150,000 depending on your growth ambitions.
Total Development Cost Breakdown
Let me put this together with real numbers for different scenarios.
Scenario 1: MVP with Outsourced Team
| Category | Cost |
|---|---|
| Development (Backend, Frontend, Mobile) | $350,000 |
| Infrastructure & Hosting (Year 1) | $60,000 |
| Compliance & Legal | $60,000 |
| Design & UX | $50,000 |
| Third-party Integrations | $40,000 |
| Marketing & Launch | $50,000 |
| Total Year 1 | $610,000 |
Timeline: 12-14 months with a team of 8-10 developers.
Scenario 2: Full-Featured App with Outsourced Team
| Category | Cost |
|---|---|
| Development (Backend, Frontend, Mobile, Advanced Features) | $600,000 |
| Infrastructure & Hosting (Year 1) | $100,000 |
| Compliance & Legal | $80,000 |
| Design & UX | $100,000 |
| Third-party Integrations | $80,000 |
| Marketing & Launch | $100,000 |
| Total Year 1 | $1,060,000 |
Timeline: 16-18 months with a team of 12-15 developers.
Scenario 3: Enterprise-Level App with US-Based Team
| Category | Cost |
|---|---|
| Development (Backend, Frontend, Mobile, Premium Features) | $1,200,000 |
| Infrastructure & Hosting (Year 1) | $150,000 |
| Compliance & Legal | $120,000 |
| Design & UX | $180,000 |
| Third-party Integrations | $100,000 |
| Marketing & Launch | $150,000 |
| Total Year 1 | $1,900,000 |
Timeline: 14-16 months with a team of 15-18 developers.
See How We've Transformed Healthcare Solutions
From pharmacy apps to psychiatric platforms to enterprise EHR systems—Zenesys has delivered SOC 2 certified, HIPAA-compliant healthcare solutions that improve patient care and streamline operations. Explore our case studies to see real-world examples of healthcare innovation.
Explore Our Healthcare PortfolioWhy You Need More Than the Development Cost
Year 2 and Beyond Costs
Building the app is 40% of the work. The other 60% happens after launch.
Ongoing maintenance costs are typically 15-20% of development costs annually. That's around $90,000-$200,000 yearly depending on your scenario.
Feature additions and updates take another 20-30% of development costs. Users expect new features every quarter, and competitive apps keep improving. Budget around $120,000-$300,000 annually for new features.
Customer support team is essential. You need in-app chat support, email support, and phone support. A small support team costs $40,000-$80,000 annually.
Server costs grow as users grow. Expect infrastructure costs to increase 20-40% annually as your user base expands.
Marketing continues. Initial launch marketing is just the beginning. User acquisition costs are constant. Budget $100,000-$300,000+ annually for ongoing marketing.
Compliance updates happen regularly. New regulations emerge. Security standards evolve. Budget $10,000-$20,000 annually for compliance updates.
Summary of Yearly Costs
- Maintenance: $90,000 - $200,000
- Feature Updates: $120,000 - $300,000
- Customer Support: $40,000 - $80,000
- Server Scaling: +20-40% annually
- Marketing: $100,000 - $300,000+
- Compliance Updates: $10,000 - $20,000
Year 2 total operational cost: $370,000 - $800,000.
By year three, you're likely spending $400,000 - $1,000,000 annually just to keep the app running and competitive.
Team Location Impact on Your Budget
Average Developer Salaries by Region (2025)
Where you hire your team changes everything. Let me show you the salary comparison.
| Role | India | Eastern Europe | Southeast Asia | US/Canada | Western Europe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senior Backend Dev | $45K | $65K | $50K | $150K | $140K |
| Senior Frontend Dev | $40K | $60K | $45K | $140K | $130K |
| Mobile Developer | $35K | $55K | $42K | $130K | $125K |
| QA Lead | $25K | $40K | $30K | $90K | $85K |
| DevOps Engineer | $50K | $70K | $55K | $160K | $150K |
The cost difference is real. Building with an India-based team costs 40-60% less than a US team. But what about quality? That's where experience matters.
An experienced Indian development agency with a proven track record delivers comparable quality to US teams. However, you need to vet them carefully. Check their portfolio. Read client reviews. Ask for references from healthcare app projects.
An inexperienced cheap team delivers poor quality. You'll spend more fixing bugs than you saved on development. Choose quality over price.
Hidden Costs Everyone Forgets
Security Audits and Penetration Testing
You can't launch a healthcare app without security verification. Third-party security firms conduct penetration tests to find vulnerabilities. Budget $15,000-$40,000 for security audits before launch. This isn't optional—it's essential.
Healthcare Domain Expert Consultation
Building a healthcare app requires understanding medical terminology, healthcare workflows, and clinical requirements. Consulting with healthcare domain experts costs $5,000-$20,000. They ensure your app matches real-world healthcare processes.

Regulatory Submission and Approvals
Some healthcare apps require government approvals. Submitting applications and working through approval processes takes time and costs money. Budget $10,000-$30,000 for regulatory submissions.
Change Requests and Scope Creep
Most projects exceed their original budget because of change requests. Your stakeholders see the app taking shape and want new features. This happens. Budget 15-20% extra ($90,000-$380,000) in our scenarios for inevitable scope changes.
Post-Launch Support
Bugs emerge after launch. Users report issues. The development team needs to fix problems quickly. Budget $5,000-$15,000 monthly for the first three months post-launch just for bug fixes and urgent support.
How the MVP Strategy Changes Your Budget
An MVP (Minimum Viable Product) is smart thinking. It lets you validate your idea before investing millions.
MVP Features vs. Full App
MVP includes only essential features:
- User registration and authentication
- Medicine search and browsing
- Shopping cart and checkout
- Basic order tracking
- Customer support chat
- Payment gateway integration
Full app adds:
- Doctor consultations
- Diagnostic test booking
- Health records storage
- Medicine reminders
- Insurance integration
- Prescription management
- Health articles and education
- Health tracking tools
- AI recommendations
- Video consultations
The MVP costs $250,000-$500,000. The full app costs $1,000,000-$3,000,000+.
MVP Timeline
Building an MVP takes 6-8 months with a team of 5-7 developers. This gives you time to test the market before committing to the full build.
Why MVP Makes Sense
Launching your MVP lets you gather real user feedback. You learn what features users actually want. You discover problems you didn't anticipate. You validate that users will pay for your service. Then, armed with real data, you build the full app with confidence.
Many startups waste money building features nobody wants. The MVP approach prevents this waste.
Choosing Between Development Models
Development Team Options
You have three main options: in-house team, outsourced agency, or hybrid model.
In-House Development Team
Advantages:
- Full control over the team and process
- Easier communication and feedback loops
- Team becomes invested in long-term success
- Proprietary knowledge stays in-house
Disadvantages:
- Highest cost option ($2,000,000-$4,000,000 per year for a full team)
- Long hiring timeline before actual development starts
- You need to provide benefits, equipment, and office space
- Hard to scale team size quickly
Best for: Large companies with established budgets and long-term vision.
Outsourced Agency
Advantages:
- Lowest cost option (40-60% savings compared to in-house)
- Immediate access to experienced developers
- Faster time to market
- No hiring or management overhead
Disadvantages:
- Less direct control over day-to-day work
- Communication challenges across time zones
- Quality depends on agency selection
- Potential language barriers
- Knowledge transfer happens at project end
Best for: Startups and small companies with limited budgets looking to validate ideas quickly.
Hybrid Model
Advantages:
- Keeps core team in-house (2-3 senior developers)
- Outsources non-core work (QA, design, specific modules)
- Balances cost and control
- Flexibility to scale up or down
Disadvantages:
- Requires strong in-house technical leadership
- Coordination between in-house and outsourced teams can be complex
- Moderate cost (middle ground between in-house and fully outsourced)
Best for: Growing companies that want to build internal expertise while controlling costs during the growth phase.
The Timeline Realistic Breakdown
Months 1-2: Planning and Architecture
You define requirements, design the database architecture, plan the development process, and hire the team. No code is written yet.
Months 3-6: Core Development
Developers build the backend, database, and basic frontend. Work is happening but nothing is visible to end users yet.
Months 7-9: Feature Development and Integration
Backend and frontend come together. APIs are integrated. Payment gateways are connected. The app starts looking like an actual product.
Months 10-12: Mobile Development and Testing
Mobile apps are built for iOS and Android. QA testing begins in earnest. Bugs are found and fixed.
Months 13-14: Final Testing and Optimization
Security audits happen. Performance is optimized. Final bugs are squashed. The app is prepared for launch.
Month 15: Launch
The app goes live on app stores and the web. Initial support is intensive. Users report bugs. The team fixes them quickly.
Most delays happen in months 10–12 when everything needs to work together. This is where projects go over budget and timeline.
Cost Variations by App Complexity
Healthcare apps range widely in complexity. Let me break it down.
Level 1: Simple Pharmacy App
Features: Medicine search, shopping, delivery tracking, basic user accounts.
Development cost: $200,000 - $400,000
Timeline: 6-8 months
Team size: 5-7 developers
Examples: Online medicine shops with basic functionality.
Level 2: Healthcare Platform (Like TATA 1MG)
Features: Pharmacy, doctor consultations, diagnostics, health records, prescription management.
Development cost: $800,000 - $1,500,000
Timeline: 14-16 months
Team size: 12-15 developers
Examples: Full-service healthcare platforms, telemedicine + pharmacy combinations.
Level 3: Enterprise Healthcare Network
Features: Everything in Level 2 plus hospital integration, insurance processing, AI diagnostics, real-time health monitoring, advanced analytics.
Development cost: $1,500,000 - $3,000,000+
Timeline: 18-24 months
Team size: 15-25 developers
Examples: Hospital networks, health insurance platforms, healthcare marketplaces.
The complexity increases costs exponentially. Level 3 isn't twice as expensive as Level 1—it's 7-10 times more expensive.
Why TATA 1MG Costs So Much More
TATA 1MG's actual development cost probably exceeded $5,000,000.
They built it with a large in-house team over 2+ years. They integrated with hundreds of pharmaceutical distributors and connected with diagnostic centers across India.
They developed custom algorithms for medicine recommendations, insurance integration systems, and a complex backend to handle thousands of daily orders.
Beyond development, they invested heavily in compliance, security, and scalability from day one. They weren’t building an MVP — they were building an enterprise-grade infrastructure.
They also had first-mover advantage costs. Back in 2014–2015, Indian healthcare tech had few established frameworks or best practices, so TATA 1MG had to innovate from scratch.
Now, in 2025, things are different. You can learn from their journey — use proven technologies, modern frameworks, and ready-to-integrate APIs to move faster and build smarter.
How to Reduce Development Costs Without Sacrificing Quality
Strategy 1: Start with MVP
Don't build everything at once. Start with the core features that solve your users' main problem. This reduces initial costs by 50–70%.
Strategy 2: Use Existing Solutions and Platforms
Don't build from scratch. Use healthcare platforms, payment processors, and analytics tools that already exist. This saves months of development time.
Strategy 3: Leverage Low-Code Development Tools
Low-code platforms (like Bubble, FlutterFlow, or specialized healthcare platforms) reduce development time and cost by 30–40%. You sacrifice some flexibility for speed and cost.
Strategy 4: Choose Your Team Wisely
An experienced Indian development team costs 40% less than a US team but delivers similar quality. The savings are real and legitimate.
Strategy 5: Hire Gradually
Don't hire your entire team on day one. Start with a small core team (3–4 developers). Grow as the project progresses. This spreads costs over time and prevents overstaffing.
Strategy 6: Use Open-Source Technologies
Build on proven open-source platforms instead of proprietary software. This reduces licensing costs by thousands annually.
Strategy 7: Automate Repetitive Tasks
Use automation for testing, deployment, and monitoring. This reduces the need for manual QA and DevOps work, lowering your team size and costs.
Strategy 8: Outsource Non-Core Functions
Outsource design, QA, and specific integrations to freelancers or specialized agencies. Keep core development in-house. This balances cost and control.
How You can fund Your Healthcare App Project
Building a healthcare app requires significant capital. Here's how companies typically fund these projects.
Bootstrapping (Using Your Own Money)
You fund it yourself. This is risky but gives you complete control. Most bootstrap founders start with an MVP ($250,000–$500,000) rather than the full app.
Venture Capital Funding
You pitch investors and raise funding. This works if you have a compelling idea and solid team. Early-stage VC funding typically ranges from $500,000 to $2,000,000. This funding covers development plus two years of operations.
Angel Investors
Individual investors provide early-stage funding ($100,000–$500,000). They're usually entrepreneurs or successful professionals who want to help founders while earning returns.
Government Grants and Programs
India's government supports healthcare tech startups through various programs. You can access grants, tax benefits, and subsidized infrastructure. Research programs like Startup India, NASSCOM, and healthcare-specific initiatives.
Bank Loans and Credit Lines
Traditional financing is harder for tech startups but possible if you have collateral or revenue. Some banks offer startup loans specifically for tech companies.
Crowdfunding
Launch a crowdfunding campaign on platforms like Kickstarter or Indiegogo. This validates your idea and funds development simultaneously.
Most successful healthcare apps combine multiple funding sources.
They start with angel funding or their own money for the MVP. Then they use traction to raise venture funding for scaling.
Questions You Should Ask Before Starting
Before you commit your budget, ask yourself these questions.
Do you have healthcare domain expertise or can you hire it?
Healthcare apps fail when founders lack healthcare understanding. You need someone on the team who understands medical workflows, regulations, and healthcare providers' needs.
Can you afford to lose this money if the idea fails?
Startups fail. This is reality. Before you invest $500,000–$1,000,000, be honest about whether you can afford to lose it.
Do you have a clear path to revenue?
How will you make money? Through commissions on medicine sales? Through premium consultations? Through insurance partnerships? Understand your revenue model before building.
Who are your competitors and how will you differentiate?
TATA 1MG has massive scale advantages. What's your competitive advantage? Speed to market? Better user experience? Specific geographic focus? Niche specialization?
Can you build the team you need?
Do you know where to find experienced healthcare developers? Can you afford their salaries? Do you have a track record that attracts talent?
Have you validated market demand?
Talk to potential users. Get pre-commitments if possible. Validate that people actually want your app before building it.
What's your path to scale?
Building the app is one thing. Growing users is another. How will you acquire users? What's your user acquisition cost? What's your growth timeline?
Timeline and How It Affects Cost of App Development
The development timeline directly impacts your budget.
Compressed Timeline (Fast Track)
If you want to launch in 8 months instead of 14 months, you need to add developers. More developers means higher costs. According to industry data, accelerating a 14-month project to 8 months increases costs by 30-50%.
Why? Because adding more developers increases communication overhead. New team members take time to onboard. Parallel development requires more coordination. The time savings aren't linear.
Standard Timeline (12-18 Months)
This is the sweet spot. It's realistic. It doesn't require heroic efforts. It doesn't compress the budget unnecessarily. Most successful healthcare apps follow this timeline.
Extended Timeline (20+ Months)
Slower timelines allow for more thorough testing and refinement. However, extended timelines increase your overall costs because the team works for longer. Infrastructure costs continue. You're supporting the project for more months.
After Launch: The Real Work Begins
Launching your app is finishing the first mile of a marathon.
First Month Post-Launch
User acquisition is your focus. You're running ads, doing PR, reaching out to press. Bug reports come in daily. Your team is fixing issues fast. Support tickets pile up. You're learning what works and what doesn't.
First Quarter Post-Launch
You're analyzing user data. You're seeing which features people use and which they ignore. You're making quick improvements. You're iterating rapidly based on feedback.
First Year Post-Launch
You're planning version 2.0 with new features. You're scaling your infrastructure as users grow. You're raising more funding for marketing and expansion. You're competing hard against established players.
Most apps that fail don't fail because of bad code. They fail because of poor market fit, weak marketing, or inability to compete. Building the app is the easy part. Growing it is the hard part.
2025 Specific Factors Affecting Your Budget
Some factors are unique to 2025 that affect your costs.
AI Integration Costs
Apps now expect AI features. AI recommendation engines, AI chatbots for support, AI diagnosis assistance—these features cost extra. Budget 10-15% more if you want AI capabilities.
Regulatory Evolution
Data protection laws are getting stricter. India's DPDP Act is relatively new. Compliance is more complex and more expensive than it was in 2023.
Inflation Impact on Development Costs
Developer salaries have increased 15-20% from 2023 to 2025. Your budget needs to reflect current market rates.
Inflation Impact on Infrastructure
Cloud hosting costs have increased slightly, but competition keeps prices reasonable. Infrastructure costs are relatively stable compared to team costs.
Remote Work Flexibility
The market now supports truly remote teams. You can hire developers from anywhere. This increases competition and slightly depresses rates in developed countries while increasing rates in developing countries.
How Zenesys Solutions Inc. Can Help You Build Your Healthcare App like TATA 1MG
Building a healthcare app requires more than just coding skills. It demands healthcare expertise, regulatory knowledge, and proven execution. Zenesys Solutions Inc brings all three to the table.
Zenesys specializes in healthcare technology solutions with a track record of delivering complex apps across India and international markets. They understand HIPAA compliance, DPDP Act requirements, and the regulatory maze that trips up most healthcare startups.
What makes Zenesys different?
They've built healthcare applications for hospitals, diagnostic centers, and pharmaceutical companies. They know the healthcare industry from the inside. They understand workflows that other development agencies miss. They anticipate regulatory challenges before they become expensive problems.
Key Strengths
- End-to-End Development
- Healthcare-Specific Expertise
- Regulatory Compliance Integration
- Scalability Architecture
- Security-First Approach
- Expert in AI-based Solutions
Cost Efficiency With Zenesys
No Hidden Costs
Zenesys provides transparent pricing. They quote based on requirements, not guesses. Change requests are handled professionally with cost adjustments only when scope genuinely changes.
Flexible Engagement Models
Fixed-price projects: Ideal for well-defined MVPs. You know the cost upfront.
Time-and-materials: Better for complex apps where requirements evolve. You pay for actual work done.
Dedicated team model: You hire a full-time remote team. Perfect for long-term projects or ongoing development.
Final Thoughts:
Total global mHealth market forecast from 2016 to 2025 in billion US dollars according to Statista.
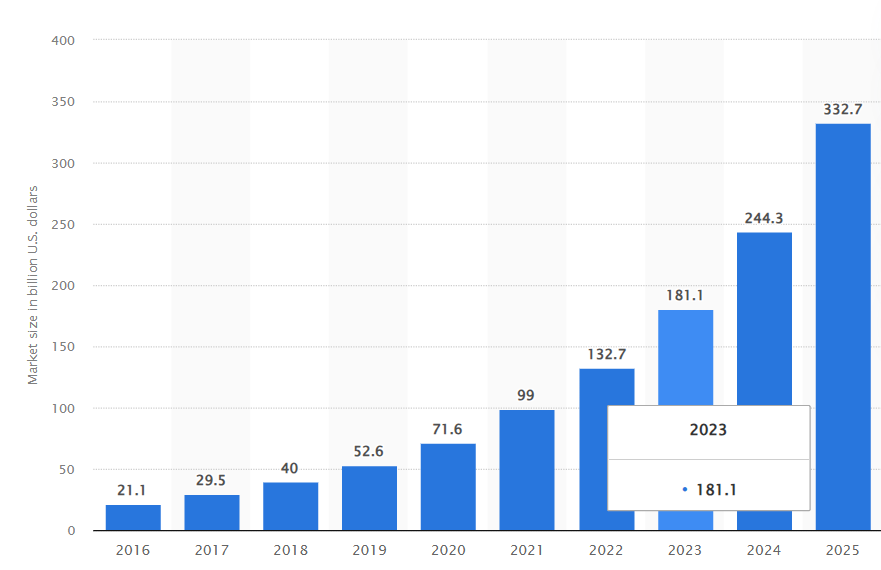
Your investment today could generate millions in returns over the next decade. But it requires patience, execution, and realistic expectations.
Start with a clear MVP. Validate your idea with real users. Grow your user base. Then invest in the full product. This approach is slower but much safer than betting your entire budget on a single launch.
The question isn't whether you should build. The question is whether you can execute better than the 500+ healthcare startups competing for the same users. If you have that conviction, the investment makes sense.


.webp?lang=en-US&ext=.webp)

.webp?lang=en-US&ext=.webp)

